Solutions To Learning Poverty
2019 Nobel Prize winning economist, Professor Michael Kremer and co-authors ground-breaking study into NewGlobe’s methodology in an African program reveals learning gains among the largest ever measured in international education.
The methodology studied in NewGlobe’s Kenya program is largely the same methodology that underpins EKOEXCEL.
Extract from study:
“The effects in this study are among the largest in the international education literature, particularly for a program that was already operating at scale.
“This study shows that attending schools delivering highly standardized education has the potential to produce dramatic learning gains at scale, suggesting that policymakers may wish to explore incorporation of standardization, including standardized lesson plans and teacher feedback and monitoring, in their own systems.”
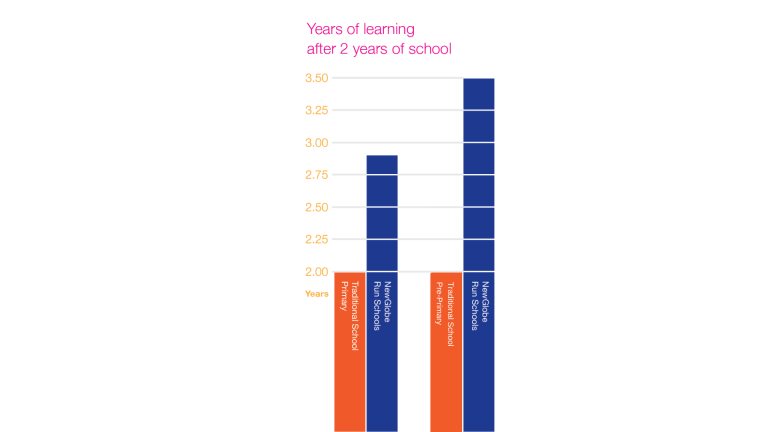
Professor Kremer and his co-authors found that primary pupils, through the equivalent of Junior Secondary School, in NewGlobe’s Kenya program gain almost an additional year of learning (0.89) under the NewGlobe integrated methodology, learning in two years what their peers learn in nearly three.
For Pre-Primary pupils the gains were even bigger. Those pupils supported by NewGlobe gained almost an additional year and half of the learning (1.48), learning in two years what pupils in other schools learn in three and a half years.
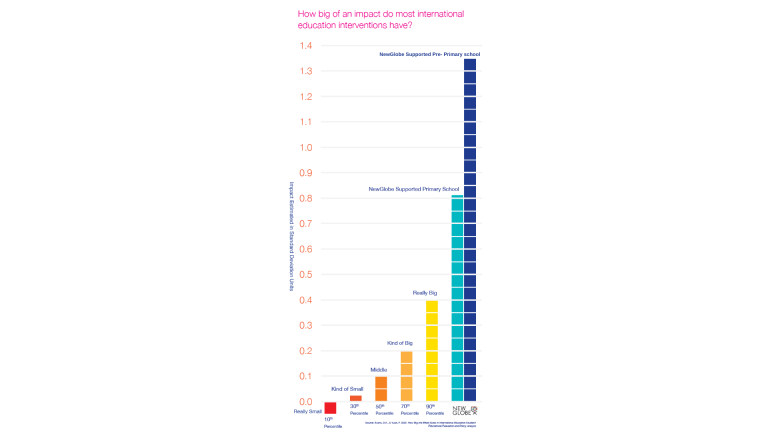
NewGlobe’s methods increased learning by 1.35 standard deviations for Pre-Primary pupils and 0.81 standard deviations for primary pupils, up through Junior Secondary School.
To put these into context, these effect sizes far exceed the 99th percentile and represent learning gains in the top 1% among large, rigorous studies in emerging markets.
If replicated at scale across public education systems, the gains would be enough to put African pupils from underserved communities on track to match their peers in countries with incomes three or four times higher.
Key Facts:
- After two years, primary pupils, up to Junior Secondary School taught using NewGlobe’s full learning system are nearly a whole additional year of learning ahead of pupils in other schools taught using ordinary methods – with learning increased by 0.81 standard deviations.
- For Pre-primary pupils, two years of teaching using NewGlobe’s methods puts them a year-and-a-half of additional learning ahead of pupils in other schools – with learning levels increased by a remarkable 1.35 standard deviations.
- In NewGlobe-supported schools, 82% of Primary 1 pupils – typically six to seven-year-olds – can read a sentence, compared with 27% of those in other schools.
- NewGlobe methods increased equity. Learning gains were greatest for pupils predicted to have the lowest performance who outperformed similar pupils attending other schools by a larger margin than their more advantaged peers.
- Girls making the same leap in learning as boys.
The two-year study is the result of a large-scale randomized control trial (RCT), including more than 10,000 pupils from low socioeconomic backgrounds.




